Hysteroscopy and Laparoscopy
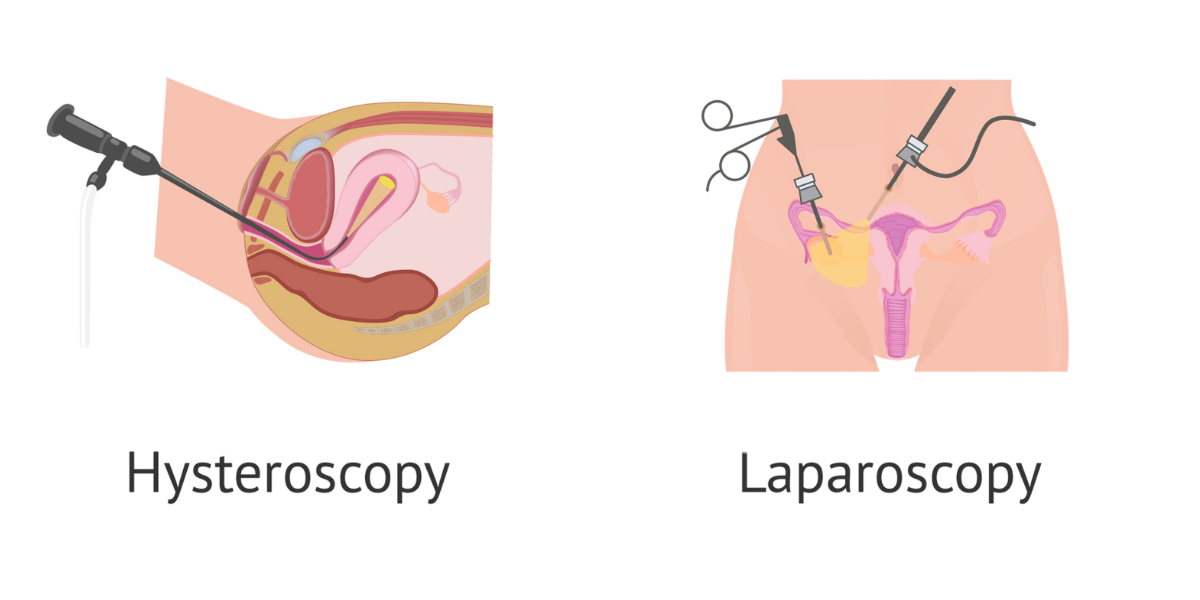
What is a Hysteroscopy?
Hysteroscopy is a minimally invasive diagnostic and therapeutic procedure used to examine the inside of the uterus. It involves the insertion of a hysteroscope—a thin, lighted tube equipped with a camera—through the vagina and cervix into the uterine cavity. Get accurate diagnosis and treatment with advanced hysteroscopy and laparoscopy procedures by Dr. Chaitali Adkar at Dr. Adkar’s Fertility Centre, Ravet, Pune. Minimally invasive solutions for fertility care.
When is a hysteroscopy suggested?
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding
Unexplained heavy or irregular menstrual bleeding is a common indication. Hysteroscopy can identify polyps, fibroids, or hyperplasia causing the bleeding.
Infertility
It helps in diagnosing intrauterine adhesions (Asherman's syndrome), uterine septum, or other anomalies affecting fertility.
Recurrent Miscarriages
Structural abnormalities like septate uterus can be detected and treated.
Endometrial Sampling
Direct visualization allows for targeted biopsy of suspicious areas, improving diagnostic accuracy.
What is Laparoscopy?
Laparoscopy, also called minimally invasive or keyhole surgery, involves the use of a laparoscope—a slender, lighted tube with a camera—to examine the organs inside the abdomen and pelvis.
When is a laparoscopy suggested?
- Chronic Pelvic Pain
- Infertility Investigation
- Ovarian Cysts and Tumors
- Ectopic Pregnancy
- Hysterectomy
- Evaluation of Pelvic Masses

