Ultrasonography
What is Ultrasonography?
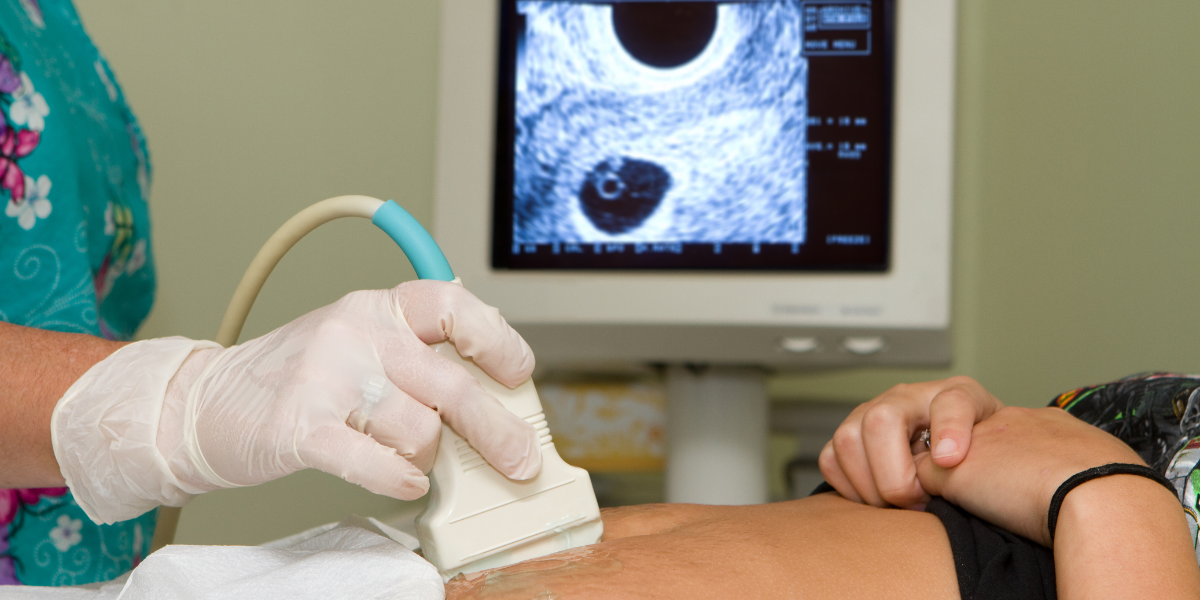
Ultrasonography (USG), commonly known as ultrasound, is a diagnostic imaging technique that uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of the internal structures of the body. This non-invasive procedure is widely used in medicine for various diagnostic and therapeutic purposes, providing detailed visuals of organs, tissues, and blood flow without the need for incisions or exposure to ionizing radiation. Schedule a fertility-focused ultrasonography (USG) with Dr. Chaitali Adkar at Dr. Adkar’s Fertility Centre, Ravet, Pune. Accurate imaging for fertility tracking and diagnosis.
Why is Ultrasonography used?
Ovarian Reserve Assessment
Evaluates the quantity and quality of a woman's remaining eggs using antral follicle count
Uterine and Endometrial Evaluation
Identifies structural abnormalities in the uterus and assesses endometrial lining
Monitoring Follicular Development
Tracks the growth of ovarian follicles during stimulation
Early Pregnancy Monitoring
Visualizes gestational sac and tracks pregnancy progression
Advantages of Ultrasonography
Non-invasive Nature
Unlike surgical procedures, ultrasonography does not require any incisions. This reduces the risk of complications and makes it a safer option for patients.
No Ionizing Radiation
Ultrasound does not use ionizing radiation, making it a safer option, especially for pregnant women and children.
Real-time Imaging
Provides immediate assessment and decision-making capabilities during procedures.
Versatility
Can examine various body parts and is instrumental in monitoring fetal development.

